|
3/07/1608
The City of
Québec
1623
Introduction of
the "seigneurial" system in Quebec (New-France).
1647
In this middle of the 17th
century, on April 11 1647, the "Compagnie de
la Nouvelle-France"
undergo the concession of a "Seigneurie" of
8 km up front by a depth 40 km to Robert Giffard.
3/06/1660
Reception of a news by a Huron that
escaped from the Iroquois, that commander
Adam Daulat, 24 years old, was kiled eight days ago.
1667
On November 2,
Robert Giffard yields his "Seigneurie" to the "Jésuites"
who name it St-Gabriel.
1693
In this end of the 17th
century, on Febuary 20 1693, the Governor of
Nouvelle-France, Louis de Buade
count of Frontenac and the intendant Champigny,
concede to Alexandre
Peuvret of Mesnu,
horseman and sieur of Gaudarville, the seigneurie of
Fossambault, named in honour of his mother
Catherine Nau of Fossambault. This
Seigneurie is situated between the Seigneuries of Neuville and
Bourg-Louis in
the west (St-Raymond parish) and Saint-Gabriel in the east. It is in the middle
of the
Seigneuries of Fossembault
and of St-Gabriel that will develop the regions of St-Patrick,
Ste-Catherine, Shannon and Valcartier (St-Gabriel).
1759
On September 18, the city of Québec falls to the hands of the British.
1760
On September 8, the city of
Montréal falls to the hands of the British.
1763
The "Traité de Paris"
puts an end to the Seven-year war opposing France and England. Canada and the
left side of the Mississippi pass from France to England. France keeps the "St-Pierre et
Miquelon" islands.
1774
By the "Acte de
Québec", London reviews the clauses of the capitulations of Québec and Montréal.
The French-Canadians conserve the French civil code and they are authorised to
speak their thong and to practice the roman religion.
1775-76
American invasion of Montréal and of Québec, Canada.
1779
The idea of a citadel
in Québec comes up in a letter of governor Haldimand to lord Townshend,
who requires the transformation of Québec into a formidable fortress.
1783
Plans by captain Twiss
of a temporary citadel in Québec.
1800
Establishment inside
the fortification walls of the Québec citadel of a service depot.
1801
Addition of a stone
powder depot (storage) at the Québec Citadel that can be considered as the origin of
the Québec Arsenal.
1804 @
1822
Addition
of four tours Martello towers to the fortifications of the Québec citadel (one
will disappear in 1900). The plans are of Holland and Twiss and the project
realised by colonel Durnford.
1821
A situation aided by the coming of Irish immigrants in Québec, a "mission" (mission,
establishment, parish, village) is established in 1821 on land concessions of
the new "Seigneur" de Fossambault, Michel-Louis (Louis-Michel)
Juchereau Duchesnay (1785-1838), the St-Patrick (St-Patrice) mission.
In 1821, a M. Owen O'Sullivan bought from Louis-M. Juchereau Duchesnay, nine lots
of land in this establishment of Saint-Patrick. This M. Owen O'Sullivan
established himself in Valcartier on May 22 1822.
1823 @ 1832
Construction
of the actual Québec Citadel with the powder depot witch recalls the arsenal's
origin.
1824
On December 7, erection
of the Ste-Catherine parish (the St-Patrick establisment).
1854
The "seigniorial" (régime féodale) regime is abolished on December 18
by a law of the "Chambre
d'assemblée du Canada-Uni", "L'Acte pour l'abolition des droits et devoirs
seigneuriaux dans le Bas-Canada".
1855
In 1855, municipalities replace the "seigneuries".
31/12/1857
Ottawa is chosen, between Québec, Montréal,
Toronto and Kingston, as the capital of the Province of Canada by queen
Victoria.
1858
The Fenians, a secret Irish society is formed
in the U.S.
04/1865
End of the american civil war.
1866-1870
The Fenians have raids in Ontario and Québec. The
Fenians where trying to capture Canada to ransom it against the freedom of Ireland. The
Canadian militia (of witch a part became the 6th battalion of the R22eR) and the British regular army where victorious.
1867
The British North American Act creates the Dominion
of Canada (Canadian confederation). Article 15 of the constitution recommend the
maintenance of a 40 000 men militia. The possibility of producing arms and
ammunition come to the attention of the authorities.
1869
Construction of the first bridge made of
wood with McCullum
beams for the crossing of the
Jacques-Cartier river at the actual site of the Shannon bridge (St-Gabriel
bridge). This bridge was
dedicated for trains of the "Compagnie du chemin à lisses (maple wood) de
Québec à Gosford".
1870
Recalling of the
British troops who leave Upper-Canada, Lower-Canada and New-Brunswick and the 60th
Regiment (Rifle Brigade) pulls out of the Citadel.
1871
Departure of the last British troops from Canadian
soil. From now on, the Dominion of Canada will assure it's own territorial defence.
12/1879
The Canadian government decrees the creation
of the "la Cartoucherie de Québec", the Québec cartrige-factory.
1880
Construction of the actual metal bridge
with Warren beams and Pratt beams for
the crossing of the
Jacques-Cartier river and is now known as the Shannon bridge (St-Gabriel bridge).
This bridge was
dedicated for trains of the "Compagnie du chemin fer de Québec et du Lac
St-Jean". The "Clarke,
Reeves and Company or Phoenix Bridge Company" who did the construction is
the same who was constructing the Quebec bridge when it crashed in 1907.
1880-81-82
Erection and maintenance of the first buildings
of the "Arsenal de Québec", the Québec Arsenal on the
"Côte du Palais" (a street). Part of the buildings of the "Arsenal de Québec" are : la redoute Dauphine (Dauphine
redoubt), une section de "les nouvelles casernes" (section of the new barracks) and l'entrepôt d'affûts de canon (the cannon-carriage
warehouse). The Dauphine redoubt was the residence of the superintendents of the Québec
arsenal from 1880 to 1958.
1882
On July 1,
opening of the St-Gabriel post office, in a section of Ste-Catherine.
1883
Sir Adolphe Caron,
minister of defence, informs Parliament that the Québec Arsenal is functioning
with an indisputable success. In twelve months, the plant workers produce a million
cartridges.
1884
The "cartoucherie de
Québec" attains a global production of 2 200 000 cartridges.
Official opening of the Québec Arsenal.
1884-1885
First confrontation by
Canadian troops in a battle abroad :
from Alexandria to Khartoum, the Sudan War and the Nile Expedition.
1885
The
Québec Arsenal
(the "cartoucherie") brings its production up to 1 500 000 cartridges in
2 months in view of a first large internal use of the canadian army since the start of
production at the arsenal in 1882 : the taming the Métis Revolt, Insurrection,
Rebellion in Western Canada (Louis Riel and Gabriel Dumont).
1886
At
the Québec Arsenal, the productivity is
double the estimate. The Federal Government adds the production of shells to the
cartridges.
1887
The shell production is
ongoing at the Québec
Arsenal.
1890
At the Québec
Arsenal, it is undertaken to fabricate cast
iron from the Trois-Rivières foundry.
1891
To proof the big shells
from the Québec Arsenal,
the shooting range is moved from the "Cove Fields" (plains
of Abraham) to l'île
d'Orléans. The first experiences are made with "cordite", a new
powder without smoke.
1895
Death of Major Oscar
Prévost, the spirit and creator of the "cartoucherie de Québec"
(Québec Arsenal), his successor, captain Frédéric-Mondelet Gaudet, will
become in 1914, the first commander of the 22nd French-Canadian
Regiment.
1899-1902
(1900)
Second confrontation by
Canadian troops in a battle abroad :
Paardeburg, the Boër War.
1901
Expansion of the factory and of the
"Cartoucherie de Québec", it becomes the Dominion Arsenal.
1902
A big demand brings the
working hours from 48 to 60 a week at the Québec Arsenal.
1903
Major J.-D.
Brousseau of the army medical service is the first permanent military doctor of
the Québec Arsenal. Dr A. E. MacIntyre, a chemist, is permanently appointed. It
is said that the Québec Arsenal administrators were always concerned at the
highest degree by the well-being and health of the personnel.
1905
On December 1, opening of the
Shannon Postal Office, in a section os Ste-Catherine.
1911
A small engineer-counselling firm is founded
by Arthur Surveyer (the S in SNC).
1912
The "Cove
Fields" (plains of Abraham) becoming the "Parc des Champs de Bataille",
the Arsenal must acquire a vast piece of land in the de Saint-Sauveur
parish to organise it's shooting range.
1914
First Shannon land expropriation by the
Valcartier military camp, at 24 km north-west of Québec city.
1914
Establishment of a military base on land of the
original Saint-Gabriel-de-Val-cartier parish (Seigneurie de St-Grabriel,
1647-1667). This
site was chosen for being at less than one day's walk from the transport ships at the
Québec naval port (harbour). Map of
Valcartier Camp 1914.
1914
First
World War
1914 @ 1918
The number
of employees at the Québec Federal
Arsenal reaches
900.
1914
At this time, Canada had 3 110 men in the
regular army, and from the fact that Great-Britain was at war, so was Canada, and in a few
weeks, more than 32 000 men and 8 000 horses were at the Valcartier camp.


1915
Valcartier military camp is used as an internment
camp for Ukrainians and other nationalities who represented a danger and a menace for
Canada. Document Document enumerating war "prisoners" names at the Valcartier camp. Valcartier concentration camp photograph in 1915.

~ 1930-1937
During the "great depression", by the introduction of the
federal program of work camps for unemployed persons, established
in Canada, the aid camp (military) of Valcartier is expanded by workers paid "20
¢" per day for works on land-clearing, renovation and construction. Some
constructions on the Valcatier base are still called by the name
"vingt cennes" or "20 ¢" in French and the workers were also
known under the wording of "Vingt cennes". The workers clear and also
prepare some land in expectation of the buildings for a new arsenal in
Val-Rose.
1935
At the nearing of the second world conflict, the Canadian government builds
new installations and ammunition factories in Val-Rose (Valcartier), while already
existing buildings are converted into an arsenal. Québec province is surnamed
"L'Arsenal du Canada", "The Canadian Arsenal".
1937
Partnership regrouping Arthur Surveyer, Emil
Nenniger et Georges Chênevert.
1938
Opening of the Val-Rose (Valcartier) factory for the filling of ammunition.
1939
Second
World War
1939
On December 1, opening of the
Valcartier Station post office, in a section of Ste-Catherine.
1940
Opening of the Saint-Malo (in Québec City) factory for the making of
cartridges and bullets.
1940
In October,
the Arsenal is transferred from the ministry of national defence to the ministry
of munition and supply.
1945
The Canadian Arsenals limited, a crown corporation is established.
1945
The National research council (NRC) establishes a defence research
laboratory, the Valcartier artillery and small arms proof and experimental establishment, adjacent to the
Canadian Arsenals.
1945
When the allies invade Germany, they discover large stocks of known
and unknown chemical arms (neuro-paralysing gas). To meet the mass production demand and
the standardisation of arms and ammunitions, the NRC (National research council) forms a
committee on ballistics and ammunition. Because of the dangerous materials, an isolated
laboratory, the Ammunitions laboratory at Valcartier became the CARDE (Canadian Armament
Research and Development Establishment of the Department of National Defence) and was
established at Valcartier near Québec.
16/10/1946
Following
quarrels over
14/12/1946
01/01/1947
Birth
of the Shannon Municipality, a section of the old Seigneurie of Fossambault.
1947
The Surveyer, Nenniger and Chênevert firm
takes up the name of SNC inc.
01/04/1947
CARDE is integrated into the Research council for defence, DRC.
1950
The Korean war procured a
revitalisation of activities for the plant of the Québec Arsenal on "côte du Palais", QC.
1951
Beginning
at the Valcartier research centre of work
for the realisation of an air to air tactical guided missile of approximately 10'
long with a 60-65 pound warhead, the "Velvet Glove"...
01/01/1953
Date giving the "right" to
citizens to sue the Canadian government (DND). Before this date the government
(and DND) had an immunity of blame for their actions.
» 1953
Appearing of the site described as the " Blue Lagoon "
or " Lagon Bleu " at CARDE, CRDV...
1957
Canada, our politicians, the ministry of national
defence, the army, send forty Canadian militaries to Nevada, not far from Area
51... They are irradiated, among others, in the Plumbbob
operation by Shot Smoky at a yield of 44kt, »
4 times the Hiroshima explosion.

1959
Beginning
at the Valcartier research centre of work
for the development of a rocket of
approximately 24'4"
long (BB1), the "Black Brant" family...
The
1960's to 1971
Beginning
at the Valcartier research centre of work
for the realisation of a rocket of
approximately 3,4' long and 2,75"
diameter, the "CRV7"...
» 1961
The "C lagoon"
at the Canadian Arsenals opens its "doors"...
1964
The Canadian Arsenals Limited
(Dominion, of Canada, federal, of Québec) conducted studies to "determine if
certain divisions of the Company should be sold to industry in order to provide
a greater scope for their manufacturing potential, while protecting
the military function for which they were designed".
1965
Second land expropriation from Shannon by the
Valcartier military camp for, between other things, the creation of a private hunting and
fishing club.
1965
On September 11, closing of the
Shannon postal office due to the expropriation (in the parish of Ste-Catherine).
1966
On December 1, changing of the
name of Valcartier Station post office to Shannon post office.
1967
It was the year of EXPO67
in Montreal and the Dominion Arsenals (Dominion Arsenal Division
of
ACL) privatise the plant at Val Rose (Valcartier) and a group of investors (Les Industries S.L.M. Inc.
with M. Georges Couture and M. Guy Godbout)
acquire the site and name it I.V.I. (Industries Valcartier Industries).
1969
The CARDE name is changed for DREV (Defence Research Establishment
Valcartier).
1980
Acquisition of the Valcartier "IVI Industries" from
"Les Industries S.L.M. Inc." by the "SNC group" and the
new name will be IVI Inc.
1986
SNC, already owner of "Les Industries Valcartier Inc.
(IVI Inc.)", acquires the assets of the "Canadian Arsenals Limited" from the
Canadian government.
01/1988
In January, the "D.S.C., Département de Santé Communautaire
(Community Health Department)" of the "Centre hospitalier de l'Université
Laval" (Laval University Hospital Centre) publishes a study report of about a hundred
page in which we can read that :
Dans le secteur industriel du pétrole et
de la chimie, il y a dans la M.R.C., les Industries Valcartier qui fabriquent des
munitions et explosifs, et que le Centre de recherche sur la défense (CRD) et la base
militaire de Valcartier étaient à inclure dans cette catégorie.
Les Industries Valcartier constituent une
des principales sources d'eaux usées industrielles de la région de Québec et la plus
importante du secteur. Les eaux usées sont déversées, après un certain traitement,
dans un affluent de la rivière Nelson qui se déverse dans la rivière St-Charles en
amont de la prise d'eau de la ville de Québec. Nous ignorons la nature exacte du système
de traitement des eaux mais ils utilisent un puisard pour recueillir les boues de
traitement, lesquelles seraient épandues deux fois l'an dans un champs du voisinage.
Les eaux usées sont susceptibles de
contenir des métaux, des solides et des huiles. Des mesures de qualité de l'eau
effectuées sur la rivière Nelson en aval du déversement industriel montrent des
augmentations des concentrations de métaux au-delà des normes de qualité.
Le Centre de Recherche sur la défense
(CRD), et les Industries Valcartier produisent des déchets dangereux. Cette dernière
produit annuellement environ 70 000 T de résidus.
Le groupe d'étude et de restauration des
lieux d'élimination des déchets dangereux a inventorié les sites d'élimination de la
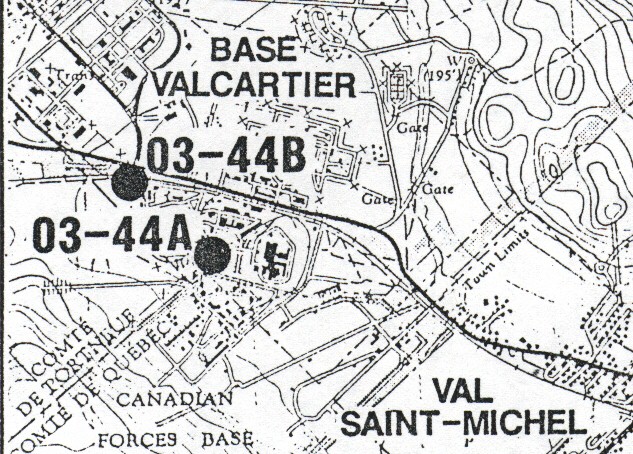
région 03. Deux sont campés dans la M.R.C. de la Jacques-Cartier, sites 44A et 44B aux
Industries Valcartier à St-Gabriel-de-Valcartier. Il s'agit du "puisard" et du
lieu d'épandage des Industries Valcartier Inc. Le "puisard" recueille des boues
de traitement contenant du cuivre, du zinc, du plomb et de l'antimoine. Il ramasse de
même des solides provenant du traitement des eaux du "réseau pluvial"
contenant des huiles et des graisses. Ces déchets sont épandus deux fois par années sur
un lieu situé sur les terrains de la compagnie. Le fond du puisard est de sable et le
sous-sol est perméable à l'infiltration des polluants (sable sur une couche d'argile).
Map of sites 03-44A
(approximately C lagoon) and 03-44B (approximately A lagoon) on SNC-Lavalin
land. This map dates of 1983/84 in a GERLED,
Groupe
d'Étude et de Restauration des Lieux d'Élimination
des Déchets Dangereux, of the Quebec ministry of environment report.
Le lieu d'épandage a été placé dans la
catégorie III car les étendus pourraient contaminer une nappe d'eau souterraine ...
La M.R.C. de la Jacques-Cartier éprouve
des risques environnementaux et sanitaires d’origine industrielle relativement
importants. Ils sont cependant uniquement localisés dans un secteur très précis, aux
limites sud-ouest de la municipalité de Valcartier (St-Gabriel). Les Industries
Valcartier Inc. et le CRD produisent des déchets dangereux et en éliminent une partie
sur des sites situés à l’intérieur du territoire et qui représentent des risques
faibles à moyens de contamination de l’environnement, mais peu de risque pour la
santé publique. Les eaux usées industrielles et les eaux d’infiltration peuvent
contaminer la nappe phréatique ainsi que les cours d’eau locaux. La nature même de
production industrielle, du type de recherche et des activités militaires du secteur
laisse croire qu’une catastrophe "technologique" peut s’y produire.
Dans un tel cas, c’est toute la région de Québec qui pourrait en être affectée.
Ceux-ci (les dépotoirs à ciel ouvert)
représentaient des risques importants pour la santé publique par leur surveillance
déficiente, la contamination possible des eaux de ruissellement et de la nappe
phréatique et par l'absence de contrôle des substances éliminées sut le dépotoir. ...
un dépotoir à ciel ouvert est encore en activité sur la base militaire de Valcartier.
Cet organisme n'est pas soumis à la législation provinciale comme tous ceux relevant du
gouvernement fédéral.
Les municipalité de
Shannon, ... Valcartier (St-Gabriel), la base militaire de Valcartier, ... puisent leur
eau de prises situés dans la zone de vulnérabilité élevée.
Il y a des sources de pollution sur le
territoire. La nappe phréatique peut se faire contaminer par divers éléments comme les
anciens dépotoirs, ... les deux sites d'élimination de déchets dangereux de Valcartier
(St-Gabriel), ... La contamination est souvent progressive dans le temps et apparaît
plusieurs années plus tard.
Nous ignorons quelles méthodes de
disposition finale des boues (de bassins, étangs et fosses) sont utilisées par ces
municipalités (incinération, rejet sauvage, lagunage, enfouissement, épandage, etc.)
Les Industries Valcartier constituent
également une source importante de pollution surtout en ce qui concerne les métaux. Des
concentrations au-delà des normes ont été relevées. La qualité de l'eau de la
rivière est très mauvaises à la hauteur de Valcartier ...
Les principaux risques
potentiels demeurent :
- les deux sites
d'élimination de déchets dangereux de Valcartier
- l'élimination des boues de fosses septiques
La qualité de l'eau potable et des eaux
de récréation inquiète plus particulièrement. Il serait pertinent d'améliorer nos
connaissances sur la qualité de l'eau potable (communautaire et privée) du secteur et de
tenter d'en évaluer l'impact réel sur la santé de la population de la région.
On observe aussi une contamination par les
métaux (rivière Nelson) ...
Conclusion et recommandations
| - |
analyse régulière des prises
d'eau privées (puits, sources etc.) |
| - |
la nécessaire protection de
l'eau souterraine compte tenu du grand nombre d'utilisateurs et des zones de
vulnérabilités élevées, ainsi que la vigilance primordiale à tout instant de la part
de tous les citoyens |
... il faudra voir à approfondir nos
connaissances et rechercher des informations supplémentaires concernant:
| - |
les rejets d'eaux usées, la
production de déchets dangereux et les deux sites d'élimination de déchets dangereux
des Industries Valcartier Inc. |
| - |
l'approvisionnement en eau du
territoire, particulièrement en ce qui concerne les eaux privées |
| - |
la qualité de l'eau potable
(communautaire et privée) du secteur et tenter d'en évaluer l'impact réel sur la santé
de la population de la région |
Il faudra voir aussi :
- à tenir à jour le profil environnemental
- rendre public le présent recueil
1988
End of sports ammunition production at the Valcartier IVI Inc. (SNC Tec)
factory.
1991
Closing of the Valcartier IVI Inc. factory.
1991
Fusion marking the history of the SNC firm ; the two biggest
engineering firms of Canada, SNC and Lavalin, unite under the name of
SNC-Lavalin.
07-1992
In a SNC-Tec environmental evaluation report, there is an excess
of 1,2 DCE in the surface water of the "C lagoon" of SNC-Tec...
11-1992
Detection of a level of 3 500 µg/L of TCE in a well at the SNC-Tec "C lagoon".
1994
Construction on the IVI Inc. (SNC Tec) site of the "maximum security
burying cell" for contaminated soils and industrial wastes.
05-1996
Detection of a level of 40 000 µg/L of TCE
in a well at the SNC-Tec 208B sector.
1997
Shannon celebrates its 50 years of existence.
18-07-1997
Detection of a level of 71 000 µg/L
of TCE in a well at the SNC-Tec 214 sector.
10/1997
"SNC Technologie inc." (a 100%
subsidiary of SNC-Lavalin) advises the DREV of the presence of TCE in the
aqueduct network supplying the base, the military family residences (PMQs) and
part of Shannon. The network is at time supplied by well P-5. Health Canada
confirms 60µg/l (60 ppb) levels, which is higher than the Canadian norm of 50
µg/l (50 ppb) and higher than the American norm of 5 µg/l (5 ppb).
10/05/1999
Transfer of infrastructures comprising the aqueduct from
Valcartier base to the Shannon municipality. Valcartier base clearly knew that
her aqueduct was contaminated with TCE and others.
31/03/2000
In the SNC-Lavalin Group Inc.
annual Notice, it is
written that SNC Tec. possesses at Valcartier a property that spans 473 acres of land with
a ground surface of 54 500 square metres.
12/2000
The TCE contamination in Shannon is
fortuitously discovered by a citizen... and it is
made public...
21/12/2000
The residents of the King’s Drive, Jacques-Cartier
and De la Station perimeter, receive from the Shannon municipality a letter containing
the following :
"La Municipalité de Shannon a récemment
été mise au fait d’une contamination possible de certains puits de notre
municipalité. Lors d’un échantillonnage de 12 puits, un dépassement de la
recommandation fédérale pour le trichloroéthylène (TCE) a été observé dans deux
puits."
Cette lettre était accompagnée d'un avis
de la Direction de la Santé publique informant les citoyens des secteurs mentionnés
"de ne pas consommer l’eau du robinet, de ventiler la chambre de bain lors de
prise de douche ou encore de faire fonctionner la hotte de la cuisinière lors de la
préparation des repas."
2001,
February 8
Tenue d'une réunion publique
convoquée par la municipalité de Shannon. C'est dans une salle remplie de plus de 500
citoyens qu'elle se déroule. Des représentants de la Santé Publique, du Ministère de
Environnement du Québec, ainsi que de la Municipalité de Shannon, se succèdent au
microphone et tentent de répondre aux questions des citoyens. La réunion se déroule
dans une atmosphère de colère car les citoyens apprennent que dès 1997, les autorités
de la Base de Valcartier savaient qu'ils étaient aux prises avec un problème de
contamination et que personne n'a cru nécessaire d’aviser la Municipalité de
Shannon et ses citoyens.
Une résidante propose la
formation d’un comité de citoyens. Le Ministère de l'Environnement s’engage à
vérifier tous les puits du coté Sud de la rivière de façon à rassurer la population.
La population est informée que des filtres au charbon activé, seront installés dans
toutes les résidences où le taux de contamination au TCE dépassera
la norme américaine de 5 µg/l ou 5ppb ou 5 parties-par-milliard (US/EPA/MCL,
United-States/Environmental Protection Agency/Maximum Contaminant Level).
2001,
February 9
At a press conference, the DND offer excuses to the Shannon
municipality for not informing the elected municipal members that they knew of the Base
well contamination since 1997.
2001,
February 14
Meeting of the Shannon citizens for the creation of a vigilance
group. The representatives of the Shannon Citizens Committee are elected and the committee
is in existence.
2001,
May 22
A public meeting is called at 19:30h,
by the Citizens' Committee with representatives of the city, health and the
environment.
|
![]()
![]()
![]()




